Understanding the Hierarchy of Industrial Automation: From Field Level to Enterprise Integration
According to EMR analysis, the global industrial automation market attained USD 192.74 billion in 2024. The market is expected to witness a CAGR of 8.6% during the forecast period of 2025-2034 to reach a value of USD 401.48 billion by 2034. Labour shortages worldwide are a critical driver for the adoption of automation technology in industries. For instance, the Chinese Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security has estimated a labour shortage of around 30 million people in 2025 in major manufacturing industries such as automobiles.
Key Statistics
- According to 2024 data, around 25% of warehouses across the globe have implemented some form of automation, with 10% using advanced automation technologies.
- In 2023, according to the International Federation of Robotics, around 4,281,585 robotic units operated in factories across the globe, an increase of 10% compared to 2022.
- According to 2022 data, automated systems will account for 25% of industrial capital spending over the next five years.
- The average return on investment (ROI) for warehouse automation is projected to be 20% within the first two years of adopting the technology, emphasising the significant financial advantages of adopting automation.
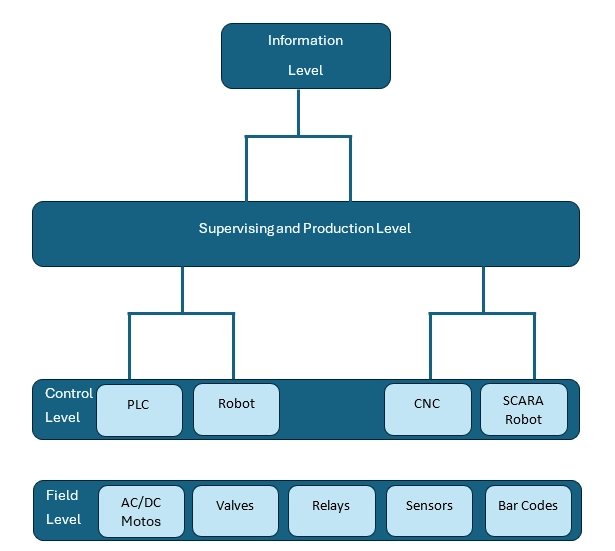
Industrial automation systems can be highly complex, comprising numerous devices operating in unison with advanced automation technologies. The below points illustrate the hierarchical structure of the automation system, highlighting the various levels within the hierarchy.
Field Level
It is the lowest level of the automation hierarchy and comprises field devices like sensors and actuators. These field devices transfer the data of processes and machines to the next higher level for monitoring and analysis. It also includes the controlling of process parameters through actuators.
Sensors convert the real-time parameters, such as temperature, flow, pressure, and level into electrical signals. This sensor data is further transferred to the controller to monitor and analyse the real time parameters. Some of the sensors used include proximity sensors, Resistance Temperature Detector (RTDs), flow meters, and thermocouples.
On the other hand, actuators convert electrical signals from controllers into mechanical actions to regulate processes. Examples of actuators include flow control valves, solenoid valves, DC motors, servo motors, pneumatic actuators and relays.
Control Level
This level encompasses various automation devices, such as CNC machines and Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), which collect process parameters from a range of sensors. The automated controllers then drive the actuators based on the processed sensor data and the defined program or control strategy. PLCs are widely recognised as reliable industrial controllers, designed to provide automatic control functions driven by sensor input.
Supervising and Production Control Level
At this level, automated devices and monitoring systems enable control and intervention functions such as Human Machine Interface (HMI), parameter supervision, production target setting, historical data archiving, and machine start/stop operations. Typically, Distribution Control Systems (DCS) or Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) HMIs are commonly employed to manage these tasks.
Information or Enterprise Level
This is the highest level of industrial automation, responsible for overseeing the entire automation system. The tasks at this level include production planning, customer and market analysis, order processing, and sales management. As such, it focuses more on commercial activities and less on technical aspects.
Industrial communication networks play a crucial role in industrial automation systems by facilitating the transfer of information across different levels. These networks are integrated into all levels of the automation system to ensure a continuous flow of data. The communication network may vary between levels, with common examples including RS485, CAN, DeviceNet, Foundation Fieldbus, and Profibus.
Thus, there is continuous information flow from high level to low level and vice-versa.
Figure: Hierarchy of an Industrial Automation System
Key Developments in the Industrial Automation Market
- In November 2024, Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR), based in Denmark, introduced the MC600 mobile collaborative robot (cobot). Designed to handle payloads of up to 600 kg, the cobot integrates the MiR600 mobile robot base with the UR20/UR30 collaborative robot arms from Universal Robots (UR), enabling the automation of complex workflows in industrial settings.
- In July 2024, Sumitomo Corp. and Dexterity Inc. formed a joint venture, Dexterity-SC Japan, aimed at accelerating the use of AI-driven robots in warehouse, supply chain, logistics, and other labour-intensive operations. With a projected 35% shortfall in transportation workers in Japan by 2030, the new venture will offer solutions for truck loading, unloading, and palletising, helping the logistics industry optimise its workforce.
- In April 2024, Pudu Robotics unveiled the PUDU T300 mobile robot as part of its expansion into industrial applications. The robot features enhanced maneuverability, a "map-and-go" function, and flexible deployment, designed to support manufacturers globally. It addresses the growing demand from industrial clients for automated, adaptable robotics solutions capable of continuous operation to achieve high production rates and improve overall operational efficiency.
- In May 2023, Renishaw, a global engineering technologies company launched a new product line tailored for the industrial automation market. The RCS product line aims to streamline the commissioning and servicing of automation technologies. It addresses key challenges in robot setup, calibration, and maintenance, focusing on improving accuracy and repeatability. The range includes the RCS L-90, RCS T-90, and RCS P-series, all supported by a specialised software suite.
Future Trends in Industrial Automation:
| Trend |
Benefits |
| Advancements in AI and Machine Learning |
The integration of AI and machine learning into industrial automation systems is revolutionising operations. These technologies allow systems to learn from data, make informed decisions, and autonomously optimise processes, resulting in enhanced efficiency and significant cost savings. |
| The Role of IoT and Smart Factories |
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming traditional factories into smart factories. By connecting machines, sensors, and systems, IoT enables real-time monitoring and control, improving efficiency, minimising downtime, and boosting productivity. |
| Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices |
Automation is driving sustainability across industries by optimising energy use, reducing waste, and supporting eco-friendly practices. As environmental regulations tighten, automation will play a critical role in helping businesses achieve their sustainability objectives. |
Conclusion:
Industrial automation is transforming business operations, driving substantial cost savings and efficiency gains. In today’s competitive landscape, where margins are narrow, it is crucial to reduce expenses without compromising on quality. Industrial automation provides a solution to this challenge, revolutionising industries by utilising technology to automate processes and boost productivity.