Biofuels primarily refer to liquid fuels and blending agents derived from biomass feedstocks. However, the term also extends to methane sourced from landfill gas, biogas, and hydrogen generated through renewable resources. While biofuels are predominantly utilised in the transport sector, they also serve as alternatives for heating and power generation. Fuels produced from biomass often align with government initiatives designed to promote or mandate the adoption of renewable energy solutions.
Biofuels are mainly used as blends with refined petroleum products like petrol, diesel, heating oil, and jet fuel. However, certain biofuels, such as drop-in biofuels, can be used directly without blending with petroleum counterparts.
Different Types of Biofuels
The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) tracks four key categories of biofuels under the federal Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS) Program:
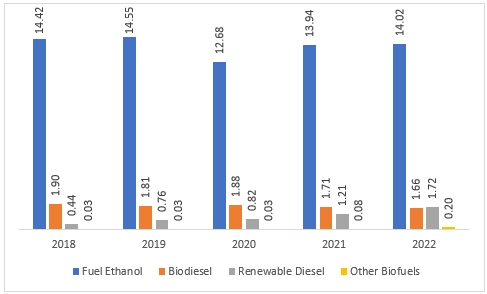
- Ethanol: Ethanol, an alcohol-based fuel blended with petrol for vehicles, dominated U.S. biofuel production (82%) and consumption (75%) in 2022.
- Biodiesel: Typically mixed with petroleum diesel, biodiesel accounted for 9% of both U.S. biofuel production and consumption in 2022.
- Renewable Diesel: Chemically like petroleum diesel, renewable diesel can be used as a drop-in fuel or blended with conventional diesel. In 2022, it represented 8% of production and 9% of consumption.
- Other Biofuels: This category includes emerging fuels such as renewable heating oil, sustainable aviation fuel, renewable naphtha, and renewable gasoline in various stages of development and commercialisation.
As awareness of global warming and sustainable living grows, biofuels have emerged as a vital alternative to traditional fossil fuels. Derived from renewable plant and crop sources, biofuels like biodiesel and ethanol are transforming transportation and energy practices.
- Boosting Energy Efficiency: Biofuel production is far more energy-efficient than fossil fuels. Research shows that biodiesel from soybeans generates 4.5 units of energy for every fossil fuel unit used in its production. Comparatively, petroleum diesel produces less than one unit of energy, highlighting biofuels as a more sustainable energy source.
- Strengthening Energy Independence: Biofuels reduce reliance on foreign oil imports by offering domestic energy solutions. Combined with other sustainable measure like incentives for hybrid vehicles and stricter fuel efficiency standards, biofuel is helping United States become more self-reliant in meeting energy demands.
- Improving Public Health: Switching to biofuels can significantly improve air quality. Traditional petrol engines emit pollutants that contribute to smog and severe health problems, including lung disease and cancer. Biofuels, such as biodiesel and biomethane, drastically reduce harmful particulates, leading to cleaner air and healthier communities.
- Cutting Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biofuels play a key role in combating global warming. Studies show that biodiesel made from recycled cooking oil can cut greenhouse gas emissions by up to 87%, significantly reducing the carbon footprint of transportation and energy systems.
- Ensuring Long-Term Sustainability: Fossil fuels are finite, but biofuels offer a renewable alternative. Made from crops that can be regrown, biofuels ensure a continuous energy supply. With diverse options like ethanol, biodiesel, and biogas, biofuels provide a sustainable path forward.
- Enhancing Engine Performance: Biofuels are compatible with most existing diesel engines, often delivering equal or better performance. Additionally, they extend engine life due to their lower viscosity and cleaner combustion properties.
North America’s Growing Shift Towards Biofuel Production:
In 2023, United States biofuel production capacity surged by 7%. This growth was primarily driven by a remarkable increase in renewable diesel and other biofuels, including renewable heating oil, sustainable aviation fuel, and renewable naphtha and gasoline.
Iowa leads U.S. biofuels production with a capacity exceeding 5.4 billion gallons per year. Fourteen states, primarily in the Midwest, Gulf Coast, and West Coast regions, collectively account for 90% of the nation’s biofuels production capacity.
Figure 1: U.S. Biofuels Production by Major Type (Billion Gallons); 2018-2022
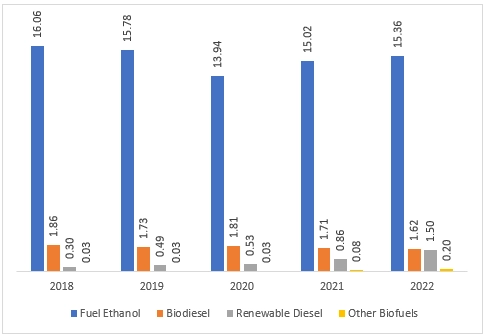
Figure 2: U.S. Biofuels Consumption by Major Type (Billion Gallons); 2018-2022
Canada remains the top destination for U.S. renewable fuel exports, accounting for over half of all ethanol and bio-based diesel exports, valued at USD 2.8 billion in 2022. Canadian imports of U.S. ethanol surged by 40% year-on-year to 1.76 billion litres, with the value rising 53% to USD 1.3 billion. This growth was fuelled by higher blending levels, particularly in Ontario, which led the country in ethanol-blended petrol consumption. This shift reflects North America’s commitment to transitioning towards cleaner energy sources. State and federal tax incentives, supportive regulatory frameworks, ongoing plant expansions, and upcoming construction projects are all accelerating the region's adoption of biofuels. As investment and innovation in the sector grow, North America is set to solidify its position as a leader in sustainable fuel production.
Government Initiatives Driving Biofuel Expansion
- USDA Biorefinery Assistance Programme: Supporting Advanced Biofuel Development: The U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Biorefinery Assistance Programme (Section 9003) offers loan guarantees to support the development, construction, and retrofitting of commercial-scale biorefineries producing advanced biofuels. The programme provides a maximum loan guarantee of USD 250 million and covers up to 50% of project costs through grants.
- Inflation Reduction Act
- In June 2023, the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) announced plans to invest up to USD 500 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to enhance the availability of domestic biofuels. This initiative aims to provide cleaner fuel options at the pump, strengthen U.S. energy independence, create new revenue streams for producers, and support economic growth in rural and agricultural communities.
- In December 2022, the USDA also allocated USD 50 million from the Inflation Reduction Act to boost the adoption and availability of higher-blend biofuels through the Higher Blends Infrastructure Incentive Program (HBIIP).
- Implementation of Canada's Clean Fuel Regulation (CFR): Enacted on 6 July 2022, the CFR aims to increase the adoption of low-carbon fuels in the transportation sector, including lower-carbon fossil fuels and biofuels with incentivised reductions in carbon intensity. The regulation is expected to drive significant shifts in Canada’s transportation fuel mix.
- Projected Fuel Consumption by 2030: Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) projects that by 2030, the CFR will lead to an additional 2.2 billion litres of low-CI diesel and 700 million litres of ethanol consumption annually.
Conclusion
North America's commitment to biofuels underscores the region's determination to achieve zero-carbon emission targets and lead the global energy transition. With robust government support, technological advancements, and increased production capacity, biofuels are transforming the energy landscape, particularly in transportation. Policies such as the USDA Biorefinery Assistance Programme, the Inflation Reduction Act, and Canada’s Clean Fuel Regulation are driving innovation, fostering economic growth, and enhancing energy independence.
As renewable energy continues to gain momentum, biofuels serve as a critical bridge to a sustainable future, offering cleaner alternatives that reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve public health, and support rural economies. By leveraging biofuels and other renewable energy solutions, North America is paving the way for a cleaner, more resilient, and sustainable energy ecosystem.





















Share